Architecture
Storage
Three-Tier Storage Architecture
Vectors flow through three storage tiers—IDMap, IVF, and OnDisk—automatically transitioning based on size and access patterns.
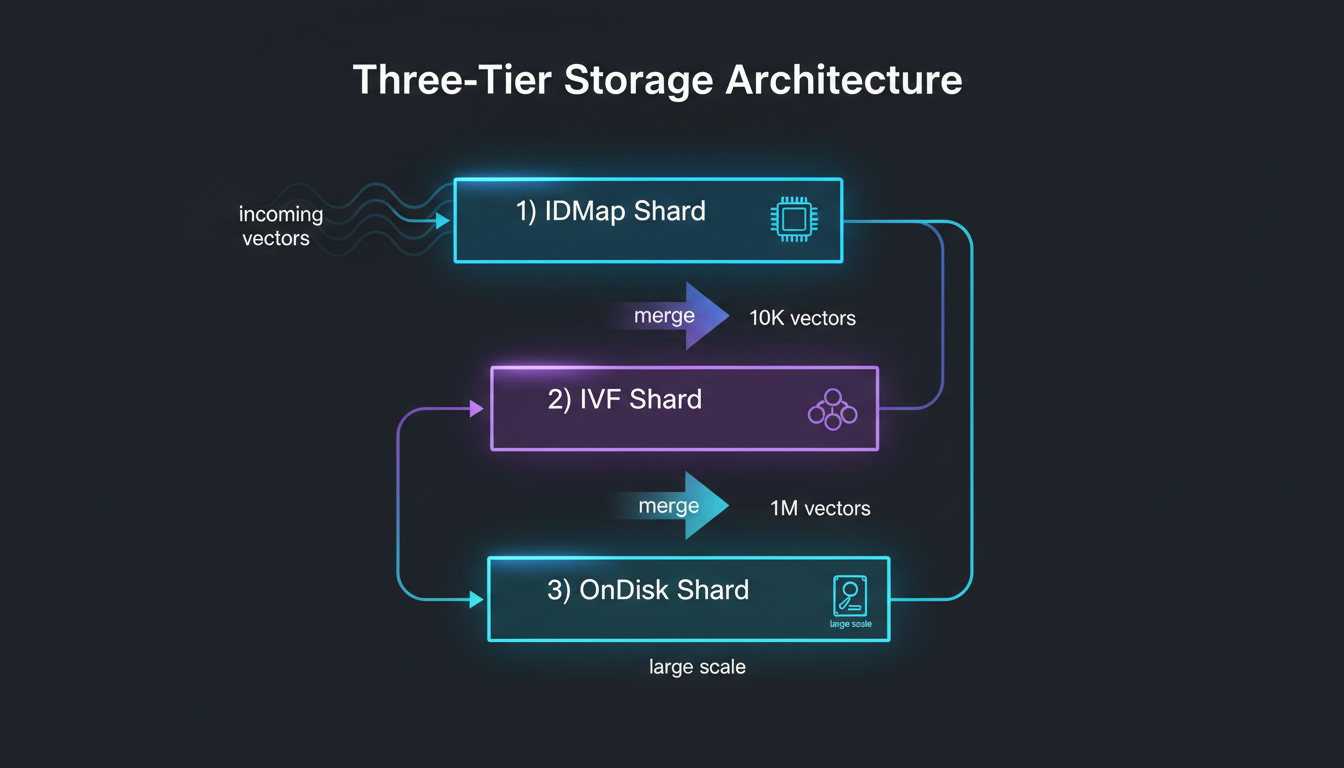
Data flow from ingestion through tier transitions

MLGraph distributed architecture with multi-node coordination
The Three Tiers
Tier 1: IDMap ShardsHot
In-memory flat storage for new vectors. Fastest writes, exact search.
- • Size limit: 10,000 vectors per shard
- • Search: Brute-force (exact)
- • Write speed: ~100,000 vec/s
- • Memory: Full vectors in RAM
Tier 2: IVF ShardsWarm
Clustered in-memory storage. Balanced read/write performance.
- • Size limit: 1,000,000 vectors per shard
- • Search: IVF (approximate, configurable recall)
- • Requires: Training on representative data
- • Memory: Centroids + inverted lists in RAM
Tier 3: OnDisk ShardsCold
SSD-backed storage. Massive scale, minimal memory.
- • Size limit: Unlimited (disk-bounded)
- • Search: IVF with disk I/O
- • Memory: Only centroids in RAM (~MB)
- • Best for: 1M+ vectors per centroid
Automatic Tiering
The SingleCentroidManagerautomatically transitions shards between tiers based on configurable thresholds:
| Transition | Trigger | Process |
|---|---|---|
| IDMap → IVF | 10K vectors | Train centroids, build inverted lists |
| IVF → OnDisk | 1M vectors | Write inverted lists to disk, keep centroids |
| Multiple OnDisk → Merged | 10M vectors across shards | Consolidate shards for efficiency |
Configuration
// SingleCentroidManager configuration
{
"tiering": {
"idmapToIvfThreshold": 10000,
"ivfToOndiskThreshold": 1000000,
"mergeThreshold": 10000000,
"training": {
"nlist": 256, // Clusters per shard
"trainingSampleSize": 50000,
"minTrainingVectors": 1000
},
"ondisk": {
"preloadCentroids": true,
"cacheInvertedLists": true,
"cacheSize": "10%" // % of total vectors
}
}
}Search Across Tiers
Queries are routed to all tiers simultaneously, and results are merged:
Query Flow
- 1. Query arrives at centroid router
- 2. Router identifies relevant centroids across all tiers
- 3. Parallel search: IDMap (exact), IVF (in-memory), OnDisk (I/O)
- 4. Results merged by distance, deduplicated by ID
- 5. Top-k returned to client