Architecture
Storage
Merge Operations Deep Dive
Understanding how vectors flow between storage tiers through IDMapToIVFMerger and IVFToOnDiskMerger operations.
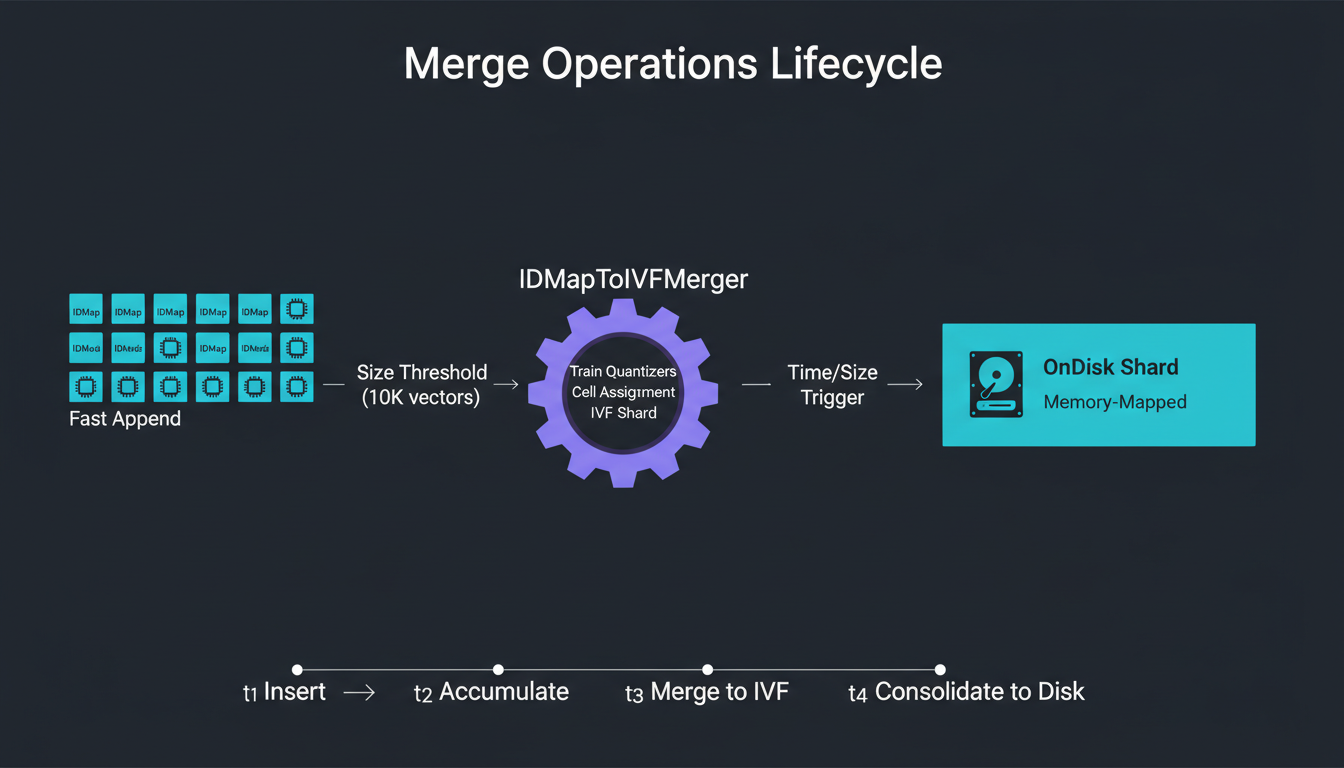
Merge process flow from IDMap through IVF to OnDisk
Merge Types
IDMap → IVF
Convert flat storage to clustered index.
- • Trigger: 10K vectors in IDMap
- • Action: Train centroids, build IVF
- • Duration: ~1s per 10K vectors
- • Non-blocking (async)
IVF → OnDisk
Move inverted lists to disk storage.
- • Trigger: 1M vectors in IVF
- • Action: Write lists to disk file
- • Duration: ~10s per 1M vectors
- • Keeps centroids in RAM
Multi-Shard Merge
Consolidate multiple shards into one.
- • Trigger: 10+ shards or 10M vectors
- • Action: Combine and re-cluster
- • Duration: ~1min per 10M vectors
- • Improves query efficiency
Compaction
Remove deleted vectors, reclaim space.
- • Trigger: 20% tombstones or scheduled
- • Action: Rewrite without deleted
- • Duration: proportional to size
- • Can run online
IDMapToIVFMerger
The most common merge: converting a flat IDMap shard to a clustered IVF shard. This requires training centroids on the data.
// IDMapToIVFMerger workflow
class IDMapToIVFMerger {
void merge(IDMapShard* source, IVFShard* target) {
// 1. Sample vectors for training
auto sample = source->sample(training_sample_size);
// 2. Train centroids using k-means
auto centroids = train_kmeans(sample, nlist);
target->set_centroids(centroids);
// 3. Assign vectors to clusters
auto assignments = assign_to_clusters(
source->get_all_vectors(),
centroids
);
// 4. Build inverted lists
for (size_t i = 0; i < source->size(); i++) {
auto cluster_id = assignments[i];
target->add_to_list(cluster_id, source->get(i));
}
// 5. Verify and swap
verify_integrity(target);
swap_shard(source, target);
}
};IVFToOnDiskMerger
// IVFToOnDiskMerger workflow
class IVFToOnDiskMerger {
void merge(IVFShard* source, OnDiskShard* target) {
// 1. Copy centroids (stay in RAM)
target->set_centroids(source->get_centroids());
// 2. Open disk file for writing
auto file = open_mmapped_file(target->path());
// 3. Write inverted lists to disk
for (size_t list_id = 0; list_id < nlist; list_id++) {
auto entries = source->get_list(list_id);
auto offset = file.write(entries);
target->set_list_offset(list_id, offset);
}
// 4. Sync and swap
file.sync();
swap_shard(source, target);
// 5. Free memory from in-memory lists
source->clear_lists();
}
};Merge Scheduling
Configuration Options
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| mergeMode | immediate, scheduled, manual | scheduled |
| mergeWindow | Time window for scheduled merges | 02:00-06:00 |
| maxConcurrentMerges | Parallel merge operations | 2 |
| mergeThrottleMBps | I/O bandwidth limit | 100 |
Best Practices
- • Schedule large merges during low-traffic periods
- • Monitor merge queue depth to avoid backlog
- • Set I/O throttling to avoid impacting queries
- • Use SSD storage for faster merge operations